We are told what to do to minimise the spread.
But rarely are we told the exact reason for needing to do what we are asked to do.
So here, I aim to give you a better understanding of the action of Covid-19 and the need for such extreme precautions.
What is Covid -19?
As we now know, the illness referred to as Covid-19 (COronaVirusDiseaseDiscovered in 2019) is caused by a novel virus.
It is caused by SARS-Cov-2 which is one of a large family of Coronaviruses, seven of which are known to affect humans.
Four of these cause a normal mild infection while SARS in 2003 and MERS in 2012 are more severe.
Once you have come into contact with the virus, it can take from 1 to 14 days for incubation and for symptoms to develop.
How does the Virus get into your Cells?
Simply put, this particular virus SARS-COV-2, uses the protein spikes found on its outside “crown” to get into the cells. It is particularly geared to binding to the cell surface of the lung, intestine, kidney, and blood vessels.
This then leads to a highly uncontrollable inflammatory response resulting in among other symptoms, high temperature, and fever.
Let’s look at what happens in the lungs:
Once the virus enters the human cell, for example, the lungs, it multiplies to produce huge numbers of new viral particles and the normal respiratory cells are damaged and die.
This is the reason why there are large numbers of microscopic particles in mucous from coughing or sneezing.
Symptoms vary from fever, cough, and shortness of breath to muscle pain, fatigue, and even pneumonia.
Some of the infected have no symptoms and it’s hard to know if they are infected.
If this is the case, this novel strain can carry on to someone else, without knowing it is happening.
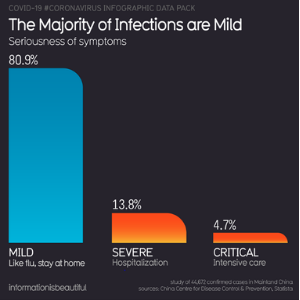
80% of people have mostly mild symptoms
15% have severe respiratory issues while
2 to 3% are critical
How does Covid-19 Spread?
The virus spreads through infected droplets via a cough or sneeze and travels through the air. It can live on surfaces for a while.
So for instance, if you sneeze it can spread for 4 m and live on surfaces..
It can live on a cardboard surface for 24 hours and on plastic and stainless steel for 2 to 3 days and I have seen references to it living on some other surfaces for up to 9 days!
It can remain in the air for three hours. So if you touch an infected surface it could well put you at risk. This is why you need to thoroughly wash your hands. And adopt extra hygiene.
Why the 1.5 m distance?
It is very important to be aware when in public to be vigilant and keep the 1.5 metre recommended distance. This is because the virus floats in the air..
The danger is, that you yourself can feel fine, but that you can affect others.
We might get a fever, dry cough, be short of breath have a sore throat, or fatigue just like the flu.
The thing is you may not have a lot of mucus!
There is generally no congestion with the dry cough.
Sometimes you can get diarrhoea and lose your sense of smell.
It can be passed on unknowingly and so it can be quite serious.
Who is most at risk of getting Covid-19?
There are certain individuals at greater risk
- Older people are at risk

Aging. Older age is also associated with declined immune system competence and this increases
the susceptibility to infection, - Immunocompromised individuals.
Those with compromised immunity/impaired immune response are at an increased risk of chronic or critical infections.
This means they have many of their body functions affected which could result in really severe infection and even increase the risk of death. - Those on chemotherapy, radiation, or immune suppressant medication are also at high risk…
- Chronic medical conditions:
Chronic illnesses affect immune function, increasing the risk and severity of infection.
It includes those with the cardiovascular or metabolic disease as well as
Those who are overweight, have hypertension, or have Type 2 diabetes.
This is because these individuals have low-grade constant inflammation in the body.
When infected, the virus binds to specific receptors and causes constant inflammation.
Then if the virus causes high inflammation they can have a serious response.
Children have been found to be at low risk because they generally do not have the same severe inflammation.
Why we need to be Careful?
The reason we all need to be extra vigilant is because some have been found to be positive for the virus while showing no symptoms, or were at the early stage of infection without symptoms yet.
If this is the case and you happen to be one of those who are positive, but show no symptoms, you could affect somebody else.
So we need to try not to pass it on to the 20% that will have more severe effects.
What is the risk of infection?
There is the incubation period of 2 to 14 days. On average it’s 5 to 6 days.
Sometimes it can take 2 to 3 weeks to get over this virus and to not be contagious.
Why is the separation period 14 days?
If you were infected then you’re contagious for 2 to 3 weeks you may have symptoms for five days
but your contagious period would be at least another one and a half weeks
So it is important for everybody’s sake to keep safe.
Especially wash hands with soap
Practice good hygiene. Frequently wash your hands.
Soap breaks down the fatty layer of the virus and stops it from being active and infecting you.
Don’t touch things and then your face. Alcohol wipes and disinfectant means you can wipe anything you’ve been touching while out.
This includes door handles, taps or anything else you’ve been in contact with.
Practice physical distancing and do not breathe on people.
Be aware that one person can give the virus to three others.
Support your own body and your Immune System
 Zinc, vitamin C, vitamin D as well as the medical mushrooms like reishi, shiitake, cordeceps support the immune system. Using herbs like elderberry Astragalus lemon balm can also provide protective preventative measures.
Zinc, vitamin C, vitamin D as well as the medical mushrooms like reishi, shiitake, cordeceps support the immune system. Using herbs like elderberry Astragalus lemon balm can also provide protective preventative measures.
These are some of the helpful ingredients.
Generally support good lifestyle and general health and wellness.
Reduce stress.
Many are suffering from stress at this time.
We know that chronic stress can weaken viral immune defenses.
Taking measures to reduce stress and support your resilience to stress is highly advisable.
Put aside a few minutes each day to engage in something you enjoy.
Engage in something positive and uplifting like music ,hobbies and exercise.
This causes change in brainwave activity and also changes your body physiology and reduces the stress burden.
Stop being bombarded with Corona Virus information.
You cannot switch on TV, the radio or social media without there being a focus on Covid-19.
Try to steer conversation with family and friends toward the positive.
Don’t get swept up in the negative hype.
Don’t stress over and obsess about the issue for six hours at a time.
It is serious, and we have to play our part, but we also need to get on with living.
Section off part of your day for updates
In stressful situations section off a part of your day to deal with it and get on with the rest of the day.
Get up to date with the new government regulations then prepare for the necessary stuff for the home.
Focus on doing more positive things
Playing board games with the family, playing with pets.
Focus on music, on hobbies because you’ now have more time.
Especially the case if you are working from home.
Pick up an instrument, paint, be creative.
When watching movies make them comedies, let them be light-hearted, let them be uplifting and enjoyable not the horrors because this can stimulate stress.
Meditation can calm you down and improve your well-being. There are many apps to use.
Apps like calm, headspace, guided meditation.
Sleep stories is an app, that I believe, can help you fall asleep.
There are many positive ways others are using to help adjust to their new way of life. Learn from them.
 Sleep and sleep well.
Sleep and sleep well.
Practised good sleep hygiene.
Wind down, dim your lights at night.
You should expose yourself to 2 hours of dim light before bedtime, so that melatonin which is your sleep hormone can be produced.
Slow down and calm down.
Take up reading a novel, doing meditation and try to get away from the phone and digital equipment.
Try to get not less than seven hours of sleep.
The most beneficial sleep is that which you get before midnight so aim to get to bed at about 2 hours before midnight.
Should you find difficulty sleeping, you can get our sleep tips.
Exercise
 Exercise is known to improve your mood, and your brain chemicals.
Exercise is known to improve your mood, and your brain chemicals.
So try to increase your heart rate for 20 minutes three times a week. It’s even better to exercise in nature because this has proven benefits and calms you down.
Taking up yoga or tai chi would be beneficial. There are many YouTube videos on these topics.
Generally look after yourself every day.
Eat regularly
-Include protein with every meal.
-Reduce the caffeine and sugar and have well rounded meals.
-Include complex carbohydrates and make sure you have regular meals.
-Increase the water.
-Water helps your mood and improves stress levels.
-Reduce the alcohol it might help you today but in the long run, you’ll probably find yourself even more stressed. Limit yourself to one two serves at a sitting a couple of times a week.
Get outside and help some vitamin D to form naturally in your body. This can help improve your immune system.
Practice gratitude.
Focus on the positives of the situation.
Start with five things to be grateful for.
Stay connected with loved ones; do this through voice calls; facetime; house party.
Our digital age means you can easily stay connected with friends and family and love ones.
These are simple ways to help improve your mood.
It will keep your stress under control .
Basically: Play your part and keep everyone safe.

Further Information can be found here: https://yourwellnesscentre.com.au/7-things-to-know-about-coronavirus-covid-19/




 Japanese mushrooms, including Cordyceps sinensis (cordyceps), Trametes versicolor (coriolus), Ganoderma lucidum (reishi) and Lentinula edodes (shiitake) enhance the body’s immune response and provide antiviral actions. Specifically, these mushrooms activate the innate immune system, triggering the production of NK cells, lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine synthesis prompts adaptive immune processes to take effect, through the promotion of B cells for antibody production, and stimulation of T cells, which mediate cellular and humoral immunity.
Japanese mushrooms, including Cordyceps sinensis (cordyceps), Trametes versicolor (coriolus), Ganoderma lucidum (reishi) and Lentinula edodes (shiitake) enhance the body’s immune response and provide antiviral actions. Specifically, these mushrooms activate the innate immune system, triggering the production of NK cells, lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine synthesis prompts adaptive immune processes to take effect, through the promotion of B cells for antibody production, and stimulation of T cells, which mediate cellular and humoral immunity.