Fish Oil – Improving Memory & Learning
Of all the supplements available on the market, fish oil, or omega 3 fatty acids (EFAs) is widely accepted as a great natural resource that helps manage cholesterol and improve cardiovascular health, but it also has a great deal of influence over the brain-behavior, and cognition.

What is it doing in the Brain?
Fish oil, or long-chain omega polyunsaturated fatty acids, have many mechanisms of action in the brain. Enhancing nervous tissue growth, replication, and proliferation of cells within the brain, increasing the fine branch-like structure at the end of nerve fibres, and the coating nerves with a myelin sheath, are some of their important functions.
Dietary intake of fatty fish isn’t always easy or desirable, so the next alternative is good quality, evidence-based supplements. Many of us are confused by the range of prices for fish oils on the market.
What is it you need to look out for?
Unfortunately, the cost comes into a question of quality very quickly, with cheaper brands offering often rancid or poor levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). It’s a good idea to do your own research, being informed and educated will help you make better choices when it comes to over-the-counter supplements.
If you’re still having doubts, speaking to your naturopath and booking in for a consultation to see if you need to be taking the supplements, is always recommended.
A typical fish oil supplement provides about 1,000 mg fish oil, containing 180 mg EPA and 120 mg DHA. Dietary supplements can contain several different forms of omega-3s, including natural triglycerides, free fatty acids, ethyl esters, re-esterified triglycerides, and phospholipids.
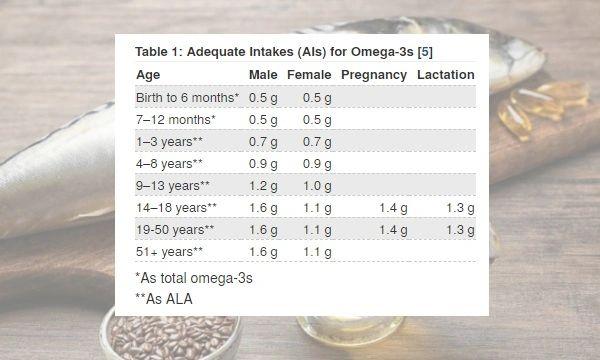
These fatty acids are not only available in fish, there are other dietary sources that give smaller quantities, in different ratios, that are also beneficial. Food to try include:
Flax or chia seeds, walnuts, soy and kidney beans, edamame as well as small amounts in eggs and milk.
Fish and seafood which contain the best amounts of EFAs:
Atlantic salmon, herring, sardines, mackerel, trout, oysters, sea bass, shrimp, lobster, and small amounts of tuna and cod.
What are the signs you might be lacking in EFAs?
Dry skin, especially around the face or arms/legs which is scaly or flaky.
Skin that cracks and peels around the fingertips or heels of the feet. Upper arm bumps, which are red in appearance but are not hot or sore.
Healing takes a longer than usual time, upwards of a week for a small scratch (that bled).
If in doubt, contact your naturopath to confirm these symptoms.
Take the step toward a healthier you!
Call 9879 9596 and book an appointment today!









Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!